GLM-Image: The First Open-Source Industrial-Grade Autoregressive Image Generation Model
On January 14, 2026, Z.AI released GLM-Image, marking a significant milestone in AI image generation technology. This groundbreaking model represents the first open-source industrial-grade discrete autoregressive image generation system, combining a 9B autoregressive module with a 7B diffusion decoder to deliver exceptional performance in text rendering and knowledge-intensive scenarios.

If you've been searching for an AI image generation model that excels at creating posters, presentations, and scientific diagrams with accurate text rendering—particularly in Chinese—GLM-Image offers a compelling solution. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about GLM-Image, from its technical architecture to practical implementation.
What Makes GLM-Image Revolutionary?
GLM-Image introduces a hybrid architecture that fundamentally differs from traditional diffusion-only models. By combining autoregressive generation with diffusion decoding, it achieves superior performance in understanding complex instructions and rendering high-fidelity details.

Hybrid Architecture Design
The model employs a two-stage generation process:
Stage 1: Autoregressive Generation (9B Parameters)
- Based on GLM-4-9B-0414 foundation model
- Generates 256-4096 compact visual tokens
- Handles text-to-image and image-to-image tasks
- Uses MRoPE positional encoding for interleaved image-text sequences
Stage 2: Diffusion Decoder (7B Parameters)
- Single-stream DiT (Diffusion Transformer) architecture
- Integrates lightweight Glyph-byT5 model for text rendering
- Outputs high-resolution images (1024px to 2048px)
- Uses flow matching as diffusion scheduling strategy
This hybrid approach allows GLM-Image to excel at global composition planning while maintaining fine detail quality—a combination that pure diffusion models struggle to achieve.
Exceptional Text Rendering Performance
Text rendering has been a persistent challenge in AI image generation. GLM-Image addresses this with remarkable accuracy:
CVTG-2k Benchmark Performance:
- GLM-Image: 91.16% word accuracy
- Seedream 4.5: 89.9% word accuracy
- Industry-leading performance in English text rendering
LongText-Bench-ZH Performance:
- 97.88% accuracy for Chinese text rendering
- Significantly outperforms competing models
- Handles complex multi-line layouts and paragraph-level semantics
These results make GLM-Image particularly valuable for creating marketing materials, educational content, and any application requiring accurate text integration.
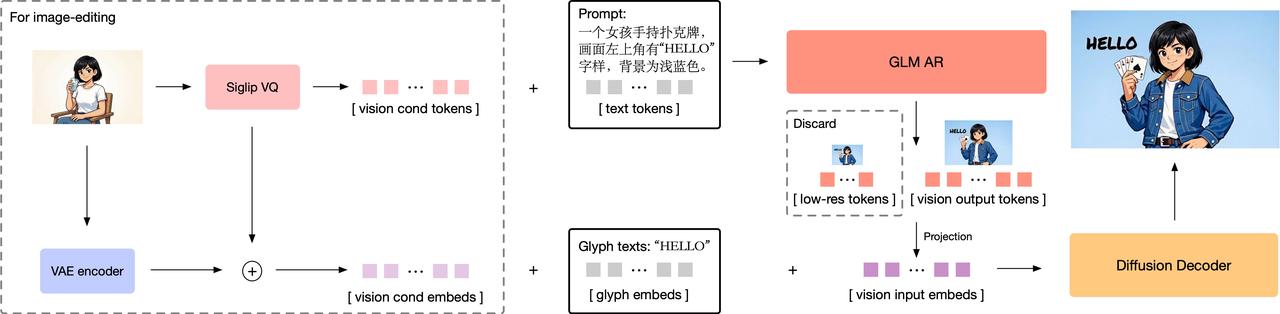
Technical Specifications and Capabilities
Understanding GLM-Image's technical foundation helps you leverage its full potential.
Model Architecture Details
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Autoregressive Module | 9B parameters (GLM-4-9B-0414 base) |
| Diffusion Decoder | 7B parameters (Single-stream DiT) |
| Output Resolution | 1024px - 2048px |
| Visual Tokenization | Semantic VQ tokenization |
| Text Enhancement | Glyph-byT5 integration |
| License | MIT (Open Source) |
Supported Generation Tasks
GLM-Image handles multiple image generation scenarios:
-
Text-to-Image Generation
- Natural language descriptions to images
- Complex multi-subject compositions
- Knowledge-intensive content creation
-
Image-to-Image Transformation
- Style transfer and artistic rendering
- Image editing and modification
- Identity-preserving generation
-
Multi-Subject Consistency
- Maintaining character consistency across images
- Coherent scene generation
- Brand identity preservation
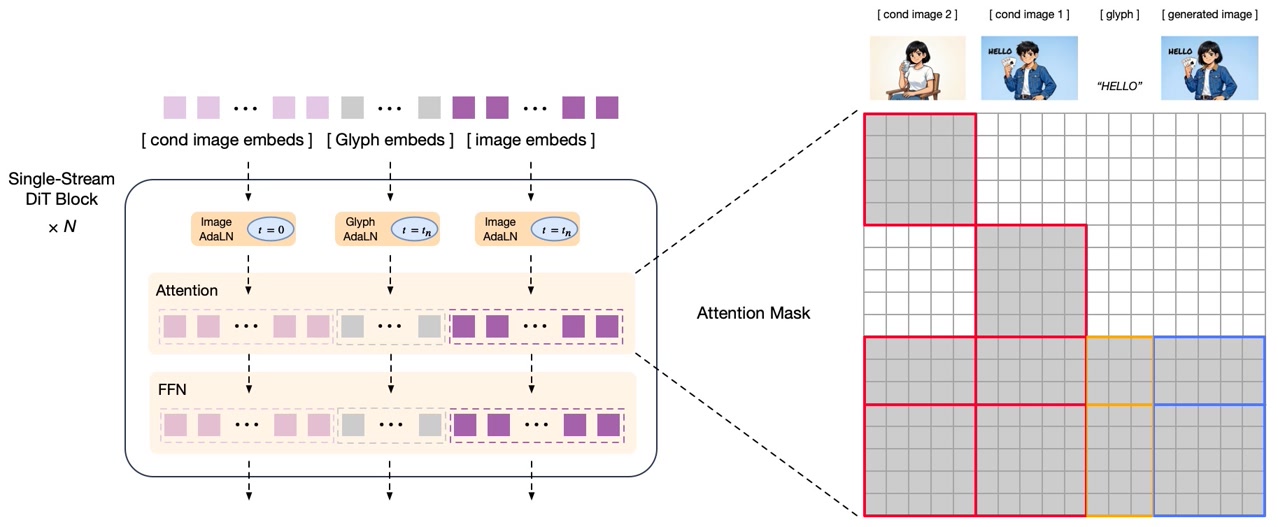
GLM-Image vs. Competing Models: Performance Comparison
To understand where GLM-Image fits in the current AI image generation landscape, let's examine how it compares to leading alternatives.
Text Rendering Comparison
| Model | CVTG-2K | LongText-Bench EN | LongText-Bench ZH | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-Image | 0.9116 | 0.9557 | 0.7877 | 0.979 |
| Qwen-Image-2512 | 0.8604 | 0.9290 | 0.7819 | 0.965 |
| Z-Image | 0.8671 | 0.9367 | 0.7969 | 0.936 |
GLM-Image leads in English text rendering (CVTG-2K and LongText-Bench EN), making it the top choice for Western markets and international applications.
General Image Generation Performance
| Model | OneIG-Bench EN | OneIG-Bench ZH | TIIF-Bench Short | TIIF-Bench Long |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-Image | 0.528 | 0.511 | 81.01 | 81.02 |
| Nano Banana 2.0 | 0.578 | 0.567 | 91.00 | 88.26 |
| Qwen-Image | 0.539 | 0.548 | 86.14 | 86.83 |
While GLM-Image doesn't lead in overall image generation scores, it excels in specific use cases:
GLM-Image Strengths:
- Text-heavy compositions (posters, infographics)
- Knowledge-intensive scenarios (educational materials, technical diagrams)
- Multi-step reasoning and inference tasks
- Chinese text rendering accuracy
When to Choose Alternatives:
- Midjourney/Flux: Artistic quality and photorealism
- DALL-E 3: Conversational interface and prompt adherence
- Stable Diffusion: Local deployment and maximum customization
- Qwen-Image: General-purpose image generation with balanced performance

Hardware Requirements and System Setup
Understanding the hardware requirements helps you plan your GLM-Image implementation effectively.
GPU Memory Requirements
GLM-Image's computational demands vary based on your chosen configuration:
Single GPU Setup:
- Minimum: 80GB+ VRAM (recommended)
- Example: NVIDIA H100 (80GB) or A100 (80GB)
- Performance: Full model capability with optimal speed
Multi-GPU Setup:
- Supported for distributed inference
- Reduces per-GPU memory requirements
- Increases overall system complexity
Resolution Constraints
All generated images must have dimensions divisible by 32:
Valid Resolutions:
- 1024×1024 (standard square)
- 1024×768 (4:3 landscape)
- 768×1024 (3:4 portrait)
- 1152×896 (custom widescreen)
Invalid Resolutions:
- 1000×1000 (not divisible by 32)
- 1920×1080 (1920 is divisible, but 1080 is not)
Performance Benchmarks
Generation time varies based on hardware and resolution:
H100 GPU (80GB):
- 1024×1024 resolution: ~64 seconds per image
- Higher resolutions: proportionally longer
Optimization Considerations:
- vLLM-Omni integration: In progress
- SGLang support: Under development
- Current inference cost: Relatively high
Getting Started with GLM-Image
There are two primary methods to use GLM-Image: through the transformers/diffusers pipeline or via SGLang for production deployments.
Method 1: Transformers + Diffusers Pipeline
This approach is ideal for development and experimentation.
Installation:
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
Text-to-Image Generation:
import torch
from diffusers.pipelines.glm_image import GlmImagePipeline
# Load the model
pipe = GlmImagePipeline.from_pretrained(
"zai-org/GLM-Image",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="cuda"
)
# Generate image
prompt = "A modern food magazine style dessert recipe illustration with elegant typography"
image = pipe(
prompt=prompt,
height=32 * 32,
width=36 * 32,
num_inference_steps=50,
guidance_scale=1.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(42),
).images[0]
image.save("output_t2i.png")
Image-to-Image Generation:
import torch
from diffusers.pipelines.glm_image import GlmImagePipeline
from PIL import Image
# Load the model
pipe = GlmImagePipeline.from_pretrained(
"zai-org/GLM-Image",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="cuda"
)
# Load reference image
image_path = "reference.jpg"
prompt = "Transform this scene into a cyberpunk style with neon lighting"
reference_image = Image.open(image_path).convert("RGB")
# Generate transformed image
output = pipe(
prompt=prompt,
image=[reference_image],
height=33 * 32,
width=32 * 32,
num_inference_steps=50,
guidance_scale=1.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(42),
).images[0]
output.save("output_i2i.png")
Method 2: SGLang for Production
SGLang provides optimized inference for production environments.
Installation:
pip install "sglang[diffusion] @ git+https://github.com/sgl-project/sglang.git#subdirectory=python"
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
Start the Server:
sglang serve --model-path zai-org/GLM-Image
API Call Example:
curl http://localhost:30000/v1/images/generations \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "zai-org/GLM-Image",
"prompt": "A professional business presentation slide with clear typography",
"n": 1,
"response_format": "b64_json",
"size": "1024x1024"
}' | python3 -c "import sys, json, base64; open('output.png', 'wb').write(base64.b64decode(json.load(sys.stdin)['data'][0]['b64_json']))"
Optimizing GLM-Image Generation Quality
Getting the best results from GLM-Image requires understanding its strengths and optimizing your workflow accordingly.
Prompt Enhancement with GLM-4.7
For optimal results, use GLM-4.7 to enhance your prompts before generation:
Basic Prompt:
"A poster about environmental protection"
GLM-4.7 Enhanced Prompt:
"A modern environmental protection poster featuring a vibrant green Earth surrounded by renewable energy symbols (solar panels, wind turbines), with bold sans-serif typography stating 'Protect Our Planet' in emerald green, clean minimalist design with white background, professional graphic design style"
The enhanced prompt provides specific details about composition, typography, colors, and style—elements that GLM-Image excels at rendering.
Sampling Parameters
GLM-Image uses specific default parameters that work well for most scenarios:
Default Configuration:
do_sample=Truetemperature=0.9top_p=0.75num_inference_steps=50guidance_scale=1.5
When to Adjust:
- Lower temperature (0.7): More consistent, predictable results
- Higher temperature (1.0): More creative, varied outputs
- Fewer steps (25-30): Faster generation, slightly lower quality
- More steps (75-100): Higher quality, longer generation time
Best Use Cases for GLM-Image
GLM-Image performs exceptionally well in specific scenarios:
1. Marketing Materials
- Posters with prominent text elements
- Infographics with data visualization
- Social media graphics with captions
- Advertisement designs with brand messaging
2. Educational Content
- Scientific diagrams with labels
- Technical illustrations with annotations
- Presentation slides with clear typography
- Instructional materials with step-by-step text
3. Knowledge-Intensive Scenarios
- Historical recreations with accurate details
- Technical documentation illustrations
- Academic poster presentations
- Research visualization with complex data
Common Issues and Solutions
Understanding potential challenges helps you troubleshoot effectively.
Memory Management
Issue: Out of memory errors during generation
Solutions:
- Reduce resolution to 1024×1024 or lower
- Use multi-GPU setup to distribute memory load
- Close other GPU-intensive applications
- Monitor VRAM usage during generation
Resolution Errors
Issue: "Resolution must be divisible by 32" error
Solution:
- Verify both width and height are multiples of 32
- Use standard resolutions: 1024×1024, 1024×768, 768×1024
- Calculate custom resolutions: (desired_size // 32) × 32
Text Rendering Quality
Issue: Text appears blurry or incorrect
Solutions:
- Use GLM-4.7 to enhance prompts with specific typography details
- Increase num_inference_steps to 75-100
- Specify font style, size, and color in prompt
- Avoid overly complex text layouts in single generation
Future Development and Roadmap
GLM-Image continues to evolve with ongoing optimization efforts:
Current Development:
- vLLM-Omni integration for faster inference
- SGLang optimization for production deployments
- Memory efficiency improvements
- Extended resolution support
Community Resources:
Conclusion
GLM-Image represents a significant advancement in AI image generation, particularly for applications requiring accurate text rendering and knowledge-intensive content creation. Its hybrid autoregressive-diffusion architecture delivers exceptional performance in specific use cases, making it an invaluable tool for marketing professionals, educators, and content creators.
While the hardware requirements are substantial for local deployment, the model's open-source nature and MIT license ensure accessibility for research and commercial applications. For those seeking immediate access without infrastructure investment, platforms like ZImage.run provide production-ready GLM-Image capabilities with professional features and multi-model support.
As the AI image generation landscape continues to evolve, GLM-Image's focus on text rendering accuracy and knowledge-intensive scenarios positions it as a specialized tool that complements rather than competes with general-purpose models. Whether you're creating educational materials, marketing campaigns, or technical documentation, GLM-Image offers capabilities that address real-world challenges in AI-generated imagery.
Sources:
- Z.AI GLM-Image Blog
- Hugging Face GLM-Image Model
- GitHub GLM-Image Repository
- AI Image Generation Model Comparison 2026